Friday, May 31, 2013
Configuration Primary Windings Delta Secondary
Above Is The Field Or Power Wiring Diagram.
American Motion Technology Offered Leadshine 863s42 Nema 34 3 Phase.
George Ulanet Company Heaters Thermostats Heating Elements.
Plc Programming For 3 Phase Motor Starting.
44356d1329715747 3 Phz Motor Wiring Leg High 3 Phase Wiring Jpg.
And There You Have It Not Really Much More Difficult Than Single.
Using Single Phase Transformers To Create 3 Phase Systems Basics.
Enabling 3 Phase Motor Operates With Single Phase Supply Circuit.
Configuration 2 Three Primary Windings In Delta And Three Secondary.
Three Phase Transformer Circuits Polyphase Ac Circuits.
Labels:
configuration,
delta,
primary,
secondary,
windings
Tuesday, May 14, 2013
Garden Tractor Wiring Diagram Parts List Manual Parts Book
Testing The Alternator.
System Circuit And Wiring Diagram 98 02 Circuit Schematic.
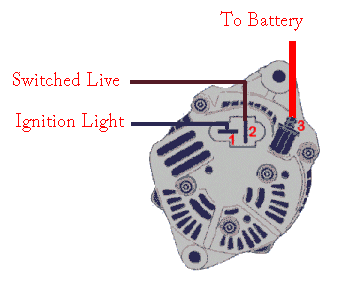
Jam S Tiger Avon Wiring A Nippon Denso Alternator.
Alternator Wiring Diagram 1978 80 Vehicles.
Chevy Truck Under Hood Wiring Diagram.
About Honda Cb400 And Cb450 Wiring Diagram And Schematics Here.
Garden Tractor Wiring Diagram Parts List Manual Parts Book.
Lexus Sc400 Charging Circuit And Wiring Diagram Circuit Schematic.
Hilux Pickup Power Window Control System Connectors And Wiring Diagram.
1997 Chevrolet Malibu Wiring Diagram And Electrical System Circuit.
Monday, May 13, 2013
Battery Voltage Indicator Circuit
Connecting this circuit to the battery of your vehicle, you will always know at a glance the approximate voltage available. An indication of battery voltage is useful to the motorist for monitoring the batterys capacity to deliver current, and as a check on the efficiency of the dynamo or alternator. Threshold voltages of the Leds are set by means of two Zener Diodes (D6 & D10) plus two further Diodes wired in series (D4, D5 and D8, D9 respectively) adding a step of about 1.3V to the nominal Zener voltage.
Parts:
R1 = 1k
R2 = 100K
R3 = 1k
R4 = 3.3K
R5 = 3.3K
R6 = 1k
R7 = 3.3K
R8 = 3.3K
Q1 = BC547
Q2 = BC547
Q3 = BC557
D1 = Red Led
D2 = Amber Led
D3 = 1N4148
D4 = 1N4148
D5 = 1N4148
D6 = BZX79C10
D7 = Green Led
D8 = 1N4148
D9 = 1N4148
D10 = BZX79C12
Notes:
* Red LED D1 is on when battery voltage is 11.5V or less. This indicates a low battery charge. * Amber LED D2 is on when battery voltage is comprised in the 11.5 - 13.5V range. This indicates that the battery is good if the motor is off. When motor is running, this indicates no charge from dynamo or alternator. * Green LED D7 is on when battery voltage is 13.5V or more. This indicates a normal condition when motor is running and dynamo or alternator is charging.
Continue Read...
Parts:
R1 = 1k
R2 = 100K
R3 = 1k
R4 = 3.3K
R5 = 3.3K
R6 = 1k
R7 = 3.3K
R8 = 3.3K
Q1 = BC547
Q2 = BC547
Q3 = BC557
D1 = Red Led
D2 = Amber Led
D3 = 1N4148
D4 = 1N4148
D5 = 1N4148
D6 = BZX79C10
D7 = Green Led
D8 = 1N4148
D9 = 1N4148
D10 = BZX79C12
Notes:
* Red LED D1 is on when battery voltage is 11.5V or less. This indicates a low battery charge. * Amber LED D2 is on when battery voltage is comprised in the 11.5 - 13.5V range. This indicates that the battery is good if the motor is off. When motor is running, this indicates no charge from dynamo or alternator. * Green LED D7 is on when battery voltage is 13.5V or more. This indicates a normal condition when motor is running and dynamo or alternator is charging.
Sunday, May 5, 2013
Silicon Chip Electronics
These two mounting methods were devised to protect PC boards from vibration when installed in the engine compartment of a car. They could also be used in other applications where vibration is a problem. Method 1 involves rigidly mounting the PC board inside a diecast box and then mounting the box itself to provide vibration isolation. As shown, small grommets are installed in suitably sized holes in the sides of the box.
The box is then secured to angle mounting brackets using M4 screws, washers and nylock nuts. Method 2 involves mounting the diecast case onto the chassis of the car and then mounting the PC board as shown, using M3 screws, grommets, hollow spacers and nylock nuts. In this case, the grommets are fitted into suitably sized holes in the PC board itself. Once the nuts are tightened, the PC board should be able to move slightly, relative to the box. If there is not enough space on the board to fit the grommets, then Method 1 is the way to do it.
Author: David Boyes - Copyright: Silicon Chip Electronics
Friday, May 3, 2013
Low Voltage High Current Time Delay Circuit diagram
In this circuit a LM339 quad voltage comparator is used to generate a time delay and control a high current output at low voltage. Approximatey 5 amps of current can be obtained using a couple fresh alkaline D batteries. Three of the comparators are wired in parallel to drive a medium power PNP transistor (2N2905 or similar) which in turn drives a high current NPN transistor (TIP35 or similar
The 4th comparator is used to generate a time delay after the normally closed switch is opened. Two resistors (36K and 62K) are used as a voltage divider which applies about two-thirds of the battery voltage to the (+) comparator input, or about 2 volts. The delay time after the switch is opened will be around one time constant using a 50uF capacitor and 100K variable resistor, or about (50u * 100K) = 5 seconds. The time can be reduced by adjusting the resistor to a lower value or using a smaller capacitor. Longer times can be obtained with a larger resistor or capacitor. To operate the circuit on higher voltages, the 10 ohm resistor should be increased proportionally, (4.5 volts = 15 ohms).
5 to 30 Minute Timer
Simple to build, simple to make, nothing too complicated here. However you must use the CMOS type 555 timer designated the 7555, a normal 555 timer will not work here due to the resistor values. Also a low leakage type capacitor must be used for C1, and I would strongly suggest a Tantalum Bead type. Switch 3 adds an extra resistor in series to the timing chain with each rotation, the timing period us defined as :-
Note that R1 has a value of 8.2M with S3 at position "a" and 49.2M at position "f". This equates to just short of 300 seconds for each position of S3. C1 and R1 through R6 may be changed for different timing periods. The output current from Pin 3 of the timer, is amplified by Q1 and used to drive a relay.
Parts
Relay 9 volt coil with c/o contact (1)
S1 On/Off (1)
S2 Start (1)
S3 Range (1)
IC1 7555 (1)
B1 9V (1)
C1 33uF CAP (1)
Q1 BC109C NPN (1)
D1 1N4004 DIODE (1)
C2 100n CAP (1)
R6,R5,R4,R3,R2,R1 8.2M RESISTOR (6)
R8 100k RESISTOR (1)
R7 4.7k RESISTOR (1)
Continue Read...
Timing = 1.1 C1 x R1
Note that R1 has a value of 8.2M with S3 at position "a" and 49.2M at position "f". This equates to just short of 300 seconds for each position of S3. C1 and R1 through R6 may be changed for different timing periods. The output current from Pin 3 of the timer, is amplified by Q1 and used to drive a relay.
Parts
Relay 9 volt coil with c/o contact (1)
S1 On/Off (1)
S2 Start (1)
S3 Range (1)
IC1 7555 (1)
B1 9V (1)
C1 33uF CAP (1)
Q1 BC109C NPN (1)
D1 1N4004 DIODE (1)
C2 100n CAP (1)
R6,R5,R4,R3,R2,R1 8.2M RESISTOR (6)
R8 100k RESISTOR (1)
R7 4.7k RESISTOR (1)
Wednesday, May 1, 2013
Supper Deluxe Charge Rate Limiter for Small Capacity NiCad Batteries
Here is a deluxe version of the simple charge rate limiter, using the same idea but with the ability to charge two packs simultaneously from a single wall charger. For circuit description and parts list, see the simple charger page. Since wall chargers provide about 55mA, you should not use this dual circuit to charge batteries at rates greater than 27mA (for a total of 54mA).





Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
